Fritz!Box 7530 Repeater Guide >
Fritz!Box Prioritization Categories >
If you have account queries or require assistance please contact us – we’d love to help you!
Sales 1800 28 58 28
Business Sales and Siro 1800 610 620
Customer Care 1902
Technical Support 1902
International Customers please call: +353 42 939 3300
My.Digiweb.ie is our customer web portal which provides you with access to your Digiweb accounts any-time, any-where and it’s free to use. Register today to view your recent statements, transactions, pay your bill on-line and change your contact details. You can also avail of some great special offers. You’ll need your Digiweb Account number and the email address associated with your Digiweb customer account.
You can access to your Digiweb accounts at anytime, from anywhere via My.Digiweb.ie – our customer web portal. It’s free and easy to use. Login today to view your recent statements, transactions, pay your bill on-line or manage your billing preferences.
We invite you to log into the portal and start enjoying this free service.
STEP 1 Go to my.digiweb.ie
STEP 2 Click “Sign Up”
STEP 3 Input your Digiweb account number, address and choose a password.
Please note: An e-mail address is mandatory in order to avail of the service.
STEP 4 Tick round button “I agree with Digiweb’s Terms & Conditions”
STEP 5 Click “Submit”
All customers can avail of this service. Pay your Bill using Payzone
Payzone Ireland is the largest consumer payments network in the country with over 7,000 retail agents which process a variety of electronic transactions services. As industry leader, Payzone’s technology credentials, capabilities and expertise are a particular strength of the business.
Call Customer Care on FREEPHONE 1918 or +353 42 939 3300. We can take Credit Card payments over the Phone
It is mandatory for Residential customers when connecting to sign a Direct Debit mandate. We can set up a Credit Card or Bank Direct Debit. This is the best way for customers to pay their bill. You will have 14 days to pay once the bill has issued. If you set up a CC DD, you will have 7 days to pay once their bill has issued. Direct Debits are collected each month between the 20th – 25th
To Setup a Direct Debit please Download and Complete DD Mandate Form
What Customers Need?
Customer will need their BIC and IBAN
Bank transfers can be made to:
Digiweb Limited
BANK OF IRELAND
IBAN: IE96 BOFI 9033 6540 4964 77
BIC / SWIFT CODE: BOFIIE2D
Please ensure you include your Digiweb account number on the payment.
The below system will generate IBAN and BIC codes for setting up direct Debits if a customer is not sure of their details. Simply input the account number and sort code by clicking on “Generate BIC/IBAN for Irish bank account.
click here to generate codes
Digiweb Call Charges (Standard and Discounted Call Rates) / Customer Dialled Calls (Discounted Call Rates) and Legacy Tariff Plans for Digiweb customers.
Please refer to call charges table:
Calls Within Ireland |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Peak | Off-Peak | Weekend | |
| Local Calls | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| National Calls- Discounted to Local Rate | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Northern Ireland (048 & 004428 Calls) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Ireland Mobile (All Networks) | 20.95 | 20.95 | 20.95 |
Non Geographic Numbers |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Peak | Off-Peak | Weekend | |
| Freefone (1800) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Callsave (1850) – Charge Per Call | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Lo-call (1890) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| VoIP (076) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Universal Access (0818) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Personal (0700) | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 |
| Internet (1891) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
| Internet (1892) | 4.29 | 2.44 | 2.44 |
Premium rates per call |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Peak | Off-Peak | Weekend | |
| Premium Rate 1512 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 |
| Premium Rate 1513 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 |
| Premium Rate 1514 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| Premium Rate 1515 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 |
| Premium Rate 1516 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 180.00 |
| Premium Rate 1517 | 250.00 | 250.00 | 250.00 |
| Premium Rate 1518 | 350.00 | 350.00 | 350.00 |
Premium Rate- Charge Per Minute |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Peak | Off-Peak | Weekend | |
| Premium Rate 1520 | 30.00 | 30.00 | 30.00 |
| Premium Rate 1530 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 |
| Premium Rate 1540 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 90.00 |
| Premium Rate 1550 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 |
| Premium Rate 1560 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 180.00 |
| Premium Rate 1570 | 240.00 | 240.00 | 240.00 |
| Premium Rate 1580 | 295.00 | 295.00 | 295.00 |
| Premium Rate 1590 | 350.00 | 350.00 | 350.00 |
Directory Enquiries |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Set-Up | Per Minute | ||
| Eircom National 11811 | 349.00 | 349.00 | |
| Eircom International 118118 | 349.00 | 349.00 | |
| Conduit National 11850 | 219.00 | 219.00 | |
| Conduit International 11860 | 249.00 | 249.00 | |
| Conduit National 11888 | 149.00 | 99.00 | |
| The Number National 11890 | 149.00 | 99.00 | |
International Destinations |
cents ¢ | cents ¢ | cents ¢ |
| Landline | Mobile | ||
| Afghanistan | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Albania | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Algeria | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| American Somoa | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Andorra | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Angola | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Anguilla | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Antarctica | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Antigua & Barbuda | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Argentina | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Armenia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Aruba | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Austrailia | 20.79 | 91.06 | |
| Austria | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Azerbaijan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bahamas | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bahrain | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bangladesh | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Barbados | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Belarus | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Belgium | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Belize | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Benin | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bermuda | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bhutan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bolivia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bosnia & Herzegovina | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Botswana | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Brazil | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| British Virgin Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Brunei Darussalam | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Bulgaria | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Burkina Faso | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Burundi | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Cambodia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Cameroon | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Canada | 18.19 | 18.19 | |
| Cape Verde | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Cayman Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Central African Republic | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Chad | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Chile | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| China | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Colombia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Comoros | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Congo DR | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Congo-Brazzaville | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Cook Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Costa Rica | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Croatia | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Cuba | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Cyprus | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Czech Republic | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Denmark | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Djibouti | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Dominica | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Dominican Republic | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| East Timor | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Ecuador | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Egypt | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| El Salvador | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Equatorial New Guinea | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Eritrea | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Estonia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Ethiopia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Falkland Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Faroe Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Fiji | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Finland | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| France | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| French Guiana | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| French Polynesia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Gabon | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Gambia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Georgia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Germany | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Ghana | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Gibraltar | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Greece | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Greenland | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Grenada | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guadaloupe | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guam | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guatemala | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guinea | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guinea-Bissau | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Guyana | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Haiti | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Honduras | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Hong Kong | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Hungary | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Iceland | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| India | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Indonesia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Iran | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Iraq | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Israel | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Italy | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Ivory Coast | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Jamaica | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Japan | 20.79 | 91.06 | |
| Jordan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Kazakhstan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Kenya | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Kiribati | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Korea- North | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Kuwait | 77.44 | 10.68 | |
| Kyrgyzstan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Laos | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Latvia | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Lebanon | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Lesotho | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Liberia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Libya | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Liechtenstein | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Lithuania | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Luxembourg | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Macao | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Macedonia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Madagascar | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Malawi | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Malayasia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Maldives | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mali | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Malta | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Marshall Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Martinique | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mauritania | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mauritius | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mayotte | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mexico | 18.19 | 18.49 | |
| Micronesia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Moldova | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Monaco | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Mongolia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Montenegro | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Mongolia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Montenegro | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Montserrat | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Morocco | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Mozambique | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Myanmar | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Namibia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Nauru | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Nepal | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Netherlands | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Netherlands Antilles | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| New Caledonia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| New Zealand | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Nicaragua | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Niger | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Nigeria | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Niue | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Northern Mariana Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Norway | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Oman | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Pakistan | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Palau | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Panama | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Papa New Guinea | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Paraguay | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Peru | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Phillipines | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Poland | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Portugal | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Qatar | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Reunion | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Romania | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Rwanda | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Saint Helena | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Saint Lucia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Saint Pierre & Miquelon | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| St Vincent & Grenadines | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Samoa | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| San Marino | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Sao Tome & Principe | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Senegal | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Serbia | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Seychelles | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Sierra leone | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Singapore | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Slovakia | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Slovenia | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Solomon Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Somalia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| South Africa | 63.02 | 91.06 | |
| Spain | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Sri lanka | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Sudan | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Suriname | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Swaziland | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Sweden | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Switzerland | 20.79 | 49.86 | |
| Syria | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Taiwan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Tajikistan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Tanzania | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Thailand | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Togo | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Tokelau | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Tonga | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Tunisia | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Turkey | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Turkmenistan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Tuvalu | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Uganda | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Ukraine | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| United Arab Emirates | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| United Kingdom | 14.89 | 39.95 | |
| United States | 18.19 | 18.19 | |
| Uruguay | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| US Virgin Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Uzbekistan | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Vanuatu | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Venezuela | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Vietnam | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Wallis and Fatuna Islands | 77.44 | 110.68 | |
| Yemen | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Zambia | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
| Zimbabwe | 77.44 | 237.54 | |
If you require technical assistance please contact us – we’d love to help you! Our Dedicated Technical Support is based in Dundalk, Co. Louth, Ireland.
To call us please dial 1902 Option 2
We care for our customers and work passionately to manage all service calls to a quick resolution so you will not be kept waiting. Our staff are knowledgeable, open, honest and customer centric. If you prefer self-service over contacting a support agent; please refer to our helpful Knowledge Base
Code of Practice for Complaint Handling
Digiweb is committed to ensuring that customers receive excellent customer service when contacting us.
How do I make a complaint?
If you have any issue or complaint about a Digiweb product or service your first point of contact will be with our Customer Care Team. We aim to resolve your query as quickly as possible.
How to contact Digiweb with a complaint:
Digiweb intends to follow the process below in handling complaints received from customers:
Digiweb will categorise complaints received from customers as follows:
If Digiweb is unable to resolve your complaint in accordance with the above timescales, we will use reasonable endeavours to ensure that you are informed about the expected timescale for resolution of your complaint.
If a customer has a dispute with Digiweb that is being investigated, we will not discontinue your service provided that you remit payment for the amount that both parties agree is not in dispute.
We have a dedicated team of trained Customer Care Agents in place to investigate and resolve your complaints.
If you are not happy with the Customer Care Agent or the way in which they handle your complaint you can ask to have the matter escalated to a supervisor or manager in the appropriate area. The supervisor or manager will provide you with a revised resolution timeframe. It may not be possible to speak to a supervisor immediately however they will return your call within 24 hours.
He / she will review and discuss the issue with you and try to reach a satisfactory resolution.
Where a final resolution cannot be provided within 10 working days, we will provide you with an appropriate timeframe for resolution with details of our ongoing resolution process and details for contacting Comreg. If we have not been able to resolve our complaint to your satisfaction within 10 working days then you may refer your case to Comreg .
Digiweb will keep a record of your complaint recording the following details:
In line with our data retention policy we will retain these details on our system for a minimum period of one year.
Refunds will be granted on a case by case basis and our customer care agent will contact you if eligible. Refunds can only be granted for over payment and not in lieu of a credit application for downtime or as a gesture of goodwill.
All refunds will be made in the same manner in which we received payment.
If we receive payment via Credit Card we can only refund the card that made the original payment.. If a customer pays via Direct Debit we refund them via bank transfer only. All other refunds can be made via EFT.
All refunds will be processed within 10 working days of final agreement.
Digiweb will do its utmost to resolve your complaint to your satisfaction. However, if you are not satisfied with the resolution of your complaint, you also have a right to seek independent advice from the bodies below:
Useful addresses and telephone numbers
You can seek independent advice regarding your complaint from any of the following:
Commission for Communications Regulation
Block DEF, Abbey Court, Irish Life Center, Lower Abbey Street, Dublin 1
Tel: 1890 229 668 or Fax: 01 804 9680
E-mail: consumerline@comreg.ie
Office of the Director of Consumer Affairs (ODCA)
National Consumer Agency
4 Harcourt Road, Dublin 2, Ireland, Dublin 1
Tel: 01 402 5500 or Fax: 01 402 5501
Website: www.odca.ie
Advertising Standards Authority
Ferry House, 48 Lower Mount Street, Dublin 2
Tel: 01 613 7040 Fax: 01 613 7043
E-mail: standards@asai.ie
If you require assistance please contact us – we’d love to help you! Our Dedicated Customer Care and Technical Support is based in Dundalk, Co. Louth, Ireland.
To call us please dial 1902 Option 1
We care for our customers and work passionately to manage all service calls to a quick resolution so you will not be kept waiting. Our staff are knowledgeable, open, honest and customer centric. If you prefer self-service over contacting a support agent; please refer to our helpful Knowledge Base
Phishing is the attempt to obtain personal information online and is one of the most common forms of internet fraud. If you have an email account, you’ve probably been on the receiving end of a phishing email at one stage or another. These emails are usually very believable and if you do give personal information to phishers, they can use it for financial gain or identity theft.
Phishing phone calls tend to impersonate company personnel or employees. The calls will often come from an Irish phone number in an attempt to look more genuine. The calling number is often spoofed, meaning it is not the actual number from which the call is originating.
Some customers have reported receiving fraudulent calls from individuals claiming to be a representative of Digiweb calling in relation to an issue/compromise of their broadband service. The caller may state that in order to fix the issue they need access to your PC/Laptop/device. The caller may put pressure on you to provide credit card details in order to repair or upgrade the security of the device. If your have received a phone call such as this and are concerned about your security, contact your bank immediately for information on what do next.
Digiweb will never require access to your computer or your credit/debit card details in relation to a fault/repair.
These are fraudulent emails that appear to come from a legitimate source such as a subscription service, your bank, or a utility company. Phishing emails generally contain links to spoof websites that appear to have the same look and feel as the source they claim to be. Phishers can then attempt to trick you into divulging sensitive information using a variety of methods including informing you of a supposed refund or an issue with your billing. You are then requested to:
Digiweb are aware of a series of unsolicited emails in circulation that claim to come from our services teams. We care about your safety and continuously work to raise awareness so that you can avoid becoming a victim of identity fraud. You may have received an email stating there was an issue with a payment on your most recent bill, asking you to click a link to pay the balance. This link sends you to an unauthorized third party site that closely resembles the Digiweb website but has various different URL addresses at the top of the web page. Alternatively, you may have received an email that claims that a bill is ready, that an account needs to be verified, you are due a refund or that a payment needs to be confirmed.
This is phishing sent via text messages. Like emails, they appear to come from legitimate numbers in an attempt to prompt you to supply personal information. Digiweb will NEVER ask for personal or financial information over text.
Digiweb is aware that scam calls can take on many forms, therefore, Digiweb advises consumers to be vigilant at all times.
We would advise consumers that returning calls to unknown international numbers can be costly and we advise consumers to exercise caution when they receive a missed call from such numbers.
Unfortunately there is no way to identify a scam call number, and they can resemble a very normal, familiar, geographical or international number that we would come across on a daily basis.
Article Credit: Comreg : https://www.comreg.ie/consumer-information/mobile-phone/scam-calls/
Parental Controls are designed to help protect your family from harmful content and other dangers on the internet.
With the FRITZ!Box WiFi modem and Home Media Hub from Digiweb, Parental Controls come “FREE as standard” with our Fibre Broadband product range. If you have your broadband with another provider you can still get these features from just €10 per month. The modem allows parents to set the total number of Internet hours in a day or set specific times of the day when your child can be online.
Parental Controls are available FREE as standard to Digiweb broadband customers with a Fritz!Box Modem and F-Secure SAFE.
Additional Parental Controls features and Internet Protection are available with F-Secure Internet Security – FREE for 3 Months -10 Devices. Then just €35.00 per year. Exclusively for Digiweb customers
Protect your children from harmful and/or inappropriate content on the internet by setting up the Parental Controls which come FREE as standard on the Fritz!Box Modem. Please refer to our step-by-step instructions, in the Parental Controls Setup Guide:
Email Set-up & Outlook account settings
If you have a POP account, your options will look a little different. Make sure you’re using these settings.
Unable to Send Emails due to SPAM Notice
Legacy Email service users may report an issue where their emails are not being received by other parties. If they are using our SMTP server they may being marked as spam. There are a number of factors that may cause the spam flag to be raised. The SMTP uses an variety of Algorithms usually referred to as a Bayesian probability algorithm which will calculate the probability of an email being spam. This will apply a score to an Email. Each company will assign a threshold to allow mails to pass through without being marked as spam however any email that exceeds the threshold score will be flagged and stopped by the sever. A higher score indicates the likelihood of an Email being Spam. A score of 10 or above is very likely to be spam whereas a score of 5 is likely to be spam. It is important to note that the algorithms change and update themselves constantly depending on the global reports of spam.
Once all these issues have been checked off or addressed the probability of an email being marked as spam will be much less likely and your email will be more likely to reach its destination with out issue. We cannot risk this server being blacklisted as this will result in a complete loss of email service across all Digiweb and Viatel platforms for at least 24-48 hours.
Cordless telephone is deregistered after a FRITZ!Box restart
After the FRITZ!Box is restarted, for example after a FRITZ!OS update, a cordless telephone from another manufacturer no longer connects to the FRITZ!Box automatically and must be registered again.
Note: The configuration procedure and notes on functions given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for your FRITZ!Box.
After disabling the expanded security functions, you must register your cordless telephone with the FRITZ!Box once.
Broadband Speed Factors
There are many factors that determine the speeds you receive to your device(s). If you’re experiencing speed issues please refer to the following to understand potential issues or Freephone 1800 285828 to speak with our knowledgeable technical staff who’ll be happy to take you through troubleshooting steps and offer their experience to help improve your speeds.
Factors can include:
Factors can include:
Factors can include:
Examples:
Some ways to get the best speeds are as follows:
How to improve your Wi-Fi
Boost WiFi to every room with TP-Link WiFi Extender
With wireless speeds of up to 300Mbps, you can effortlessly extend the Wi-Fi network in your home via the existing electrical circuitry and broadcast a wireless signal to share with all your Wi-Fi enabled devices in another area of your home.
You can order the TP-Link 300Mbps AV200 WiFi Powerline Extender Starter Kit from Digiweb for just €64.95
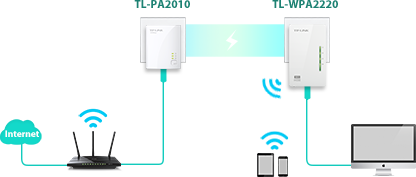
Plug and Play Easy WiFi Boost
You can set up a hassle-free Powerline network within minutes with TP-LINK’s powerline adapters, just plug in and play. Also, the adapters’ “Pair” buttons can be utilized for securing or managing multiple powerline adapters in your home powerline network.
For Technical Assistance – please dial 1902 Option 2
How to install TP-Link WiFi Extender
Need help installing your TP-Link 300Mbps AV200 WiFi Powerline Extender Starter Kit?
Need help setting up your Lightning Broadband (FTTH) Fritz!Box Modem? Please refer to our step-by-step instructions in the following Quick Start Guide:
Need help setting up your NBI FTTH Broadband Fritz!Box Modem? Please refer to our step-by-step instructions in the following Quick Start Guide.
Need help setting up your SIRO Broadband Fritz!Box Modem? Please refer to our step-by-step instructions in the following Quick Start Guide.
Need help setting up your VDS Broadband Fritz!Box Modem? Please refer to our step-by-step instructions in the following Quick Start Guide.
The broadband connection type you can get will depend on where you live. We now have 1.7 million premises passed with fibre broadband. Over 100,000 are Fibre to the Home (FTTH), your home or business may now qualify for same. Freephone 1800 285828 and we can confirm available options with you.
Alternatively, request a callback from our friendly and knowledgeable sales team who’ll answer any queries you may have at a time that suits best. For complex queries write to us:
sales@digiweb.ie
Digiweb provide internet services via several high-speed transmission technologies.
Digiweb provide internet services via several high-speed transmission technologies.
SIRO Broadband (Fibre to the Home – FTTH)
NBI Broadband (Fibre to the Home – FTTH)
Lightning FTTH Broadband (Fibre to the Home – FTTH)
Superfast Broadband (Fibre to the Cabinet – FTTC)
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
NextGen (Next Generation)
Wifiber/Nova/Ripple (Wireless)
Fibre
Made of strands of glass, fibre optic Internet provides faster, smoother service with more room for signal traffic compared to traditional copper cable wires. FTTH (Fibre to the Home) and FTTC (Fibre to the Cabinet) refer to the wiring path and configuration the signals travel. The closer the fibre optic legs reach to the final destination, the better the connection. Digiweb provide both FTTH (Fibre to the Home) and FTTC (Fibre to the Cabinet).
FTTH (Fibre to the Home) is the delivery of 100% optical fibre from Digiweb’s exchange all the way to the home, thereby replacing existing copper infrastructure such as telephone wires and coaxial cable.
The fibre optic communications path is terminated on or in the premise for the purpose of carrying communications to a single subscriber. In order to be classified as FTTH, the access fibre must cross the subscriber’s premises boundary and terminate inside the premises, or on an external wall of the subscriber’s premises, or not more than 2m from an external wall of the subscriber’s premises.
FTTH services may deliver just one application, but generally deliver several such as data and VoIP. Because the connection goes directly to individual residences, FTTH offers a higher bandwidth and speeds up to 2,000Mbps.
FTTC (Fibre to the Cabinet) is where the Fibre optic cable is run to the enabled cabinet nearest to your home, and the remaining connection to your premises is run over the existing copper cables. By replacing a large proportion of the copper cables to the cabinet with fibre, it means the speeds that can be achieved are significantly higher. FTTC can serve several customers within 1,000 feet. This is the most common fibre connection which provides a high-speed internet connection of up to 100Mbps (megabytes per second).
NextGen / DSL
NextGen / DSL (Digital subscriber line/originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. The term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology, for Internet access. DSL service can be delivered simultaneously with wired telephone service on the same telephone line. This is possible because DSL uses higher frequency bands for data. On the customer premises, a DSL filter on each non-DSL outlet blocks any high-frequency interference to enable simultaneous use of the voice and DSL services. The bit rate of Digiweb DSL services typically ranges from 24 Mbps in the direction to the customer (downstream), depending on DSL technology, line conditions, and service-level implementation.
Broadband speeds are measured in Mbps (megabits per second)
Download Speed: this is the speed with which you can receive content from the Internet. How quickly you can download a song, view a movie on Netflix, etc.
Upload Speeds: this is the speed with which you can send content. This could be sending an email, uploading photos to a website.
Most people download much more than they upload, therefore Broadband download speeds are always set to be faster than upload speeds.
What are “up to” speeds and why do we use this term?
Broadband Providers use the term ‘up to’ when selling broadband products.
This is because the broadband speeds achievable will depend on a number of factors including the broadband connection type installed, the modem/router technical capabilities, whether your devices are directly connected to the modem via network cable or connected via WiFi. Additionally, your internal network and customer devices will affect speeds achievable.
How do I know what speeds I will receive?
When you contact our sales team directly on Freephone 1800 285828 they will estimate the maximum speeds achievable based on the broadband connection type available at your address. You simply need to provide us with your Eircode or existing landline or UAN number.
The fastest broadband speeds can be achieved by ordering Digiweb SIRO Broadband (FTTH) or NBI Fibre Broadband Lightning Broadband (FTTH) broadband which are capable of delivering download speeds up to 2,000Mbps. These plans provide a 100% fibre-optic internet connection all the way to the building (fibre to the home / fibre to the building), making it a vast improvement on any other broadband infrastructure currently available in Ireland, with no copper connection at any point in the network. With fibre to the home (FTTH) you’ll have incredible speed and reliability instantly. These services are subject to network availability at your address.
Other currently used technology in Ireland is Fibre to the Cabinet (FTTC) which delivers download speeds are up to 100Mbps. Alternatively, previous technologies such as uncongested NextGen or DSL broadband provide download speeds up to 24Mbps.
These broadband services use the existing copper infrastructure such as telephone wires and coaxial cable. The speed coming down the cable is what we refer to as ‘line speed’. How far your house is from your local telephone exchange and local cabinet are speed factors when looking to understand the maximum speeds achievable to your home.
Every time you use your home broadband, you’ll be using a certain amount of data. The amount you use will depend on the activity – so for example, streaming a movie will use significantly more data than doing a quick Google search. Examples of download usage:
| Service | Usage Average | Typical Data Size |
| Web browsing | 50 web pages 30 mins | ~10MB to 13MB |
| 15 Mins with NO video streaming | ~5MB | |
| 100 text emails sent or received | ~2.5MB | |
| Music | 1 Music Track | ~5MB |
| YouTube 240p | 4 Min Music Video | ~11MB |
| YouTube 360p | 4 Min Music Video | ~20MB |
| YouTube 480p | 4 Min Music Video | ~30MB |
| YouTube 720p | 4 Min Music Video | ~90MB |
| YouTube 1080p | 4 Min Music Video | ~150MB |
| Radio Streaming | 10 Min | ~15MB |
| Google Maps | 10 Min | ~6MB |
| Netflix (Standard Definition) | 1 Hour | ~0.7GB |
| Netflix (High Definition) | 1 Hour | ~3GB |
| Netflix (Ultra High Definition) | 1 Hour | ~7GB |
| TV Watching | 15 Mins | ~45MB |
We make switching broadband providers simple. Simply Freephone 1800 28 58 28 to speak with our friendly, knowledgeable Sales team. We’ll be happy to assist you every step of the way.
You’ll need your Universal Account Number (UAN), Circuit Reference Number or Line ID if switching NBI connection. In some cases all we require is your Customer Account Number. To switch SIRO, your current provider must provide you with SIRO Account number. This information is usually listed on your broadband and/or phone bills. If you are unable to locate it, the below table should help.
Broadband Provider |
Where to find your UAN |
Contact Number |
| eir | Your UAN(s) and Account number can be found at the top of your bill on the first page. | 1901 / 1800 773 729 |
| Vodafone | Your UAN may not be on your bill, but can be obtained by contacting Vodafone directly. | 1907 / 1850 20 40 20 |
| Sky | Your UAN may not be on your bill, but can be obtained by contacting Sky directly | 0818 776 231 |
| Pure Telecom | Your UAN should be listed under “Service Description for Account”. This section is normally on page 2 of your bill. | 01 289 5555 |
| Virgin Media | Your UAN is your Virgin account number and this is generally at the top of the first page of your bill. | 1908 |
| Imagine | On page two of Imagine bills under “Charges for line rental” | 1890 92 92 92 |
How soon can I have my Digiweb service installed at my home?
As soon as you’re ready. Once you submit your phone, chat or online order, we’ll proceed. Fibre Broadband orders are completed within 4 – 6 days on average. We offer a variety of appointments, and some services do not even require you to be home as they’re completed at the network exchange, not the home.
For further explanation please call Freephone 1800 28 58 28 to speak with our friendly, knowledgeable Sales team.
Will my services be disrupted during switch?
Most times you previous provider service will be transferred to your new Digiweb service without disruption. This is called active line transfer. Active line transfer can apply to a majority of providers. In certain cases, Digiweb’s services will be a new service, based on a new line connection. In that case customers can avail of IASS Switching.
What is Internet Access Switching (IASS)?
All internet providers in Ireland should offer internet access switching and give you the option to switch your internet service when you join. If you have decided to avail of this service and you provide the relevant details to Digiweb, we will notify your old provider on your behalf to let them know that you want to cease internet service.
What information do I need to give for switching in order to avail of ?
You will need to be the account holder of your existing service and provide the following information if opting in and providing your consent for broadband switching.
Will I lose service during switching?
No, we won’t notify your old provider to cease services until your new Digiweb broadband or phone line service is live.
This a non-exhaustive list of terms relevant to broadband as defined by the European Commission.
The making available of facilities and/or services to another undertaking, under defined conditions, on either an exclusive or non-exclusive basis, for the purpose of providing electronic communications services, including when they are used for the delivery of information society services or broadcast content services. It covers inter alia: access to network elements and associated facilities, which may involve the connection of equipment, by fixed or non-fixed means (in particular this includes access to the local loop and to facilities and services necessary to provide services over the local loop); access to physical infrastructure including buildings, ducts and masts; access to relevant software systems including operational support systems; access to information systems or databases for pre-ordering, provisioning, ordering, maintaining and repair requests, and billing; access to number translation or systems offering equivalent functionality; access to fixed and mobile networks, in particular for roaming; access to conditional access systems for digital television services and access to virtual network services.
Cover the gap between tariff and costs – Access deficit arises when the tariff specified for access does not cover the cost of providing access.
A technology that enables, for example, rapid access to interactive broadband services and video on demand through copper wire used in existing local telephone loop plant, In its “2+” iteration, ADSL supports one-way transmission at bit rates up to 24 Mbps on a single pair of copper wires and enables subscribers to connect to data networks and the Internet at speeds from 50 to 200 times faster than current analogue modems operating at 28.8 Kbps.
Access Node
A technology for FTTH/FTTB (aka Ethernet point-to-point)
Those associated services, physical infrastructures and other facilities or elements associated with an electronic communications network and/or an electronic communications service which enable and/or support the provision of services via that network and/or service or have the potential to do so, and include, inter alia, buildings or entries to buildings, building wiring, antennae, towers and other supporting constructions, ducts, conduits, masts, manholes, and cabinets.
Those services associated with an electronic communications network and/or an electronic communications service which enable and/or support the provision of services via that network and/or service or have the potential to do so and include, inter alia, number translation or systems offering equivalent functionality, conditional access systems and electronic programme guides, as well as other services such as identity, location and presence service.
Broadband transmission technology which provides the backbone of the world’s telecommunications network. ATM breaks information flows into small fixed-length cells of 53 bytes. Cells of any type of traffic – voice, multimedia, data or video – can be interspersed with each other. ATM operates at speeds of 25, 155 and 622 Mbps.
Bandwidth is the capacity of a network or other communication channel for transferring data, measured in bps.
The middle part of a broadband network, connecting the local access to the core internet network. Technically the link from the cable head to the international switching centre.
Areas where at least two competing high capacity broadband network operators are present.
BEREC and the BEREC Office were created by Regulation 1211/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2009 to assist the Commission and the national regulatory authorities (NRAs) in the implementation of the EU regulatory framework for electronic communications, to give advice on request and on its own initiative to the European institutions and to complement at European level the regulatory tasks performed at national level by the regulatory authorities, all in the aim of creating an internal market for electronic communications. BEREC is composed of the 27 NRAs.
A term applied to high speed telecommunications systems, i.e. those capable of simultaneously supporting multiple information formats such as voice, high-speed data services and video services on demand. The Digital Agenda defines three levels of broadband speeds: 2, 30, and 100 Megabit per Second.
In December 2012, new rules on state aid for broadband were adopted, replacing the 2009 broadband guidelines. Main changes are the need for a step change, i.e. a substantial improvement of broadband coverage as a result of aid, Aid for minor improvements is excluded under strict conditions aid for ultrafast broadband in under-served areas, is eligible. The new rules include a technology neutral definition for fixed wireless access solutions to fall under the definition of NGA.
Refers to the rules that apply to landing a submarine cable in a country.
Capital expenditure
Content-centric networking is a term used to refer to Information-centric networking (ICN). Please see entry on ICN.
Is an internet top level domain generally used or reserved for a country (a sovereign state of a dependent territory, e.g. fr .nl).
Code-Division Multiple Access is a digital cellular technology that uses spread-spectrum techniques. CDMA does not assign a specific frequency to each user. Instead, every channel uses the full available spectrum. Individual conversations are encoded with a pseudo-random digital sequence. CDMA is a military technology first used during World War II by the English allies to foil German attempts at jamming transmissions. The allies decided to transmit over several frequencies, instead of one, making it difficult for the Germans to pick up the complete signal.
The CEF Connecting Europe Facility is the financing instrument for the Trans-European Networks for Transport, Energy and Telecommunications for 2014-2020.
Digital Services Infrastructure (DSI or CEF-DSI) refers to the part of the CEF funding that would support public interest digital service infrastructure such as electronic health records, electronic identification and electronic procurement.
The programs, activities and interactions used by owners and operators to protect their critical infrastructure.
Shielded and insultated copper cable, mainly used by caple TV companies and also for computer networks. Coaxial cable is supposed to minimise interference with electrical and radio transmissions.
The Cocom assists the Commission in carrying out its executive powers under the regulatory framework and the regulation on the .eu Top Level Domain. The Cocom exercises its function through advisory and regulatory procedures in accordance with the Council Comitology Decision. Furthermore, the Cocom provides a platform for an exchange of information on market developments and regulatory activities.
The provision of physical space and technical facilities necessary to reasonably accommodate and connect the relevant equipment of a beneficiary.
Copper is the electrical conductor used in telecommunications. The DSL technology is based on copper wires. Transmission speeds depend on the lengths and quality of the copper wire from the distribution point to the building.
The digital divide is the gulf between those parts of the population that have access to the internet and other digital technologies, and those sections of the population that do not. There is concern that as so many services (both commercial and governmental) become available online, groups without digital access (caused by, among other things, high cost, lack of skills, location, or a combination of these) will be left behind, and miss out on opportunities in life and in work.
The digital dividend refers to the radio spectrum which becomes available as a result of the switchover of terrestrial TV broadcast from analogue to digital technology which uses the spectrum more efficiently. This is a unique and once-off opportunity to boost the capacity for providing new and innovative broadcast and wireless communication services. The first step related to the 800 Mhz (790 MHz to 862 MHz) while a second phase, following the decision of WRC 12 to open the band to mobile communications, would cover the 700 MHz band.
A cable TV network solution
Digital Subscriber Line
European Commission
“Innovative” financial instruments are loans, guarantees, EU-support to project bonds, or dedicated equity funds. As compared to the traditional grant instrument, FI have the advantage of attracting more additional investment (leverage). For the Connecting Europe Facility support to the roll-out of broadband, the Commission envisions to use FI as much as possible.
(typically an MDU), a first-mile infrastructure
(from which the first-mile connection starts), a local area infrastructure
Technology aiming at replacing the technologies DSL by installing optic fiber to the consumer. Less ambitious versions are FTTC (Fibre To The Curb) and FTTB (Fibre To The Building).
Broadband network architecture using optical fibre to create a broadband network for the last mile.
A shared-access technology for FTTH/FTTB (ITU-T G.984)
Areas with only one high capacity broadband infrastructure or one infrastructure provider in place.
The Guide, issued by the European Commission in 2011, is aimed at assisting management authorities of EU funds to plan and implement broadband projects financed in the context of EU regional and rural development policies. The guide is structured around seven questions concerning policy, regulatory, investment and technological issues including the pros and cons of five different investment models for efficient and effective public-sector interventions in next-generation broadband access networks.
High-definition television
Combination of optical fibre and coaxial cable.
High-speed broadband is a broadband service provided through a Next Generation Network (NGN).
A service provided by an incumbent operator whereby a new entrant rents a high speed access path to the customer. The incumbent provides and maintains the transmission systems (e.g. ADSL modem at the local exchange) needed to provide the access path.
Extension of the UMTS standard allowing for faster data transfer.
Telecommunications organisations granted special and exclusive rights by Member States or public operator(s) which enjoyed a de facto monopoly before liberalisation.
Indefeasible right of use
e.g. a SP delivering Internet service
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations agency for information and communication technology issues, ITU coordinates the shared global use of the radio spectrum, and establishes the worldwide standards that foster interconnection of a vast range of communications systems.
The physical twisted copper pair circuit connecting the network termination point at the subscriber’s premises to the main distribution frame or equivalent facility in the fixed public telephone network. The local loop may also include optical elements. The physical circuit connecting the network termination point to a distribution frame or equivalent facility in the fixed public electronic communications network.
A service whereby a telecommunication organisation provides (shared or fully) unbundled access to its local loop to another telecommunications organisation.
A partial local loop connecting the network termination point at the subscriber’s premises to a concentration point or a specified intermediate access point in the fixed public telephone network.
The costs that are directly associated with the production of a business increment, i.e. the additional cost of supplying a service over and above the situation where the service was not provided, assuming all other production activities remain unchanged. ‘Long run’ means that all factors of production including capital equipment are variable in response to changes in demand due to changes in the volume or in the structure of production, therefore all investments are considered as variable costs.
The ‘bottom-up’ LRIC modelling approach develops a cost model starting from the expected demand in terms of subscribers and traffic; it then models the efficient network that is required to meet the expected demand, and assesses the related costs according to a theoretical network-engineering model. The purpose of a bottom-up model is to calculate the cost on the basis of an efficient network using the newest technology employed in large-scale networks. This approach differs from a top-down modelling approach, which is based on the undertaking’s accounts. In a hybrid modelling approach the bottom-up model is refined by looking at the results of the top-down model. It is also possible to check the plausibility of some of the results of the top-down model by using the bottom-up model.
High performance communication system for cellular mobile phones. Step towards 4th generation, but commonly called 4G
An apartment block
A technique of deploying cables, e.g. for broadband networks, at a lower cost than by the usual method. A micro trencher is a “small rockwheel” specially designed for work in urban area. It is fitted with a cutting wheel that cuts a microtrench with smaller dimensions than can be achieved with conventional trench digging equipment. The trench dimensions are widths ranging from about 30 mm to 130 mm, and a maximum depth of about 500 mm.Micro trenchers may also be used to install FTTx connections.
Mobile broadband is the name used to describe various types of wireless high-speed internet access through a portable modem, telephone or other device. Various network standards may be used, such as WiMAX, UMTS/HSPA, EV-DO and some portable satellite-based systems.
The MSS allow communications between satellites and mobile terrestrial equipment. Their use can range from high-speed internet access to mobile television and radio and emergency communications. Mobile satellite services cover a large part of the EU’s territory, thereby reaching millions of EU citizens across borders. They can ensure access for all Europeans to new communication services, not only in metropolitan areas, but also rural and less populated regions.
Network neutrality is the principle that all electronic communication passing through a network is treated equally. That all communication is treated equally means that it is treated independent of (i) content, (ii) application, (iii) service, (iv) device, (v) sender address and (vi) receiver address. Under the reformed Telecom Rules, national telecoms regulatory authorities will in particular be required to promote “the ability of end users to access and distribute information or run applications of their choice”. This will contribute to strengthening the “neutral character” of the internet in Europe.
Access networks which consist wholly or in part of optical elements and which are capable of delivering broadband access services with enhanced characteristics (such as higher throughput) as compared to those provided over already existing copper networks. In most cases NGAs are the result of an upgrade of an already existing copper or co-axial access network.
Ability of a network or an information system to resist, at a given level of confidence, accidental events or malicious actions. Such events or actions could compromise the availability, authenticity, integrity and confidentiality of stored or transmitted data as well as related services offered via these networks and systems.
In relation to interconnection and/or access, an obligation of non-discrimination ensures that an operator applies equivalent conditions in equivalent circumstances to other undertakings providing equivalent services, and provides services and information to others under the same conditions and of the same quality as it provides for its own services, or those of its subsidiaries or partners.
Operates the active equipment and delivers SP’s services to the end users
The body or bodies charged by a Member State with any of the regulatory tasks assigned in the Regulatory framework for telecommunications.
The physical point at which a subscriber is provided with access to a public communications network; in the case of networks involving switching or routing, the NTP is identified by means of a specific network address, which may be linked to a subscriber number or name.
On line behavioural advertising (OBA) uses tracking cookies. Hence, pursuant to EU privacy laws such practices must comply with the requirement to obtain users’ consent.
DG CONNECT is facilitating stakeholder discussion on a proposed self-regulation on online behavioural advertising which should provide transparent, consent based, user-friendly mechanisms with effective enforcement. Stakeholders involved include advertising associations, ICT industry and associations and consumer representatives.
Is an undertaking providing or authorised to provide a public communications network or an associated facility
Operational expenditure
An optical fibre is a fiber made of glass or plastic allowing the transmission of information over light over long distances with very high data rates.
Public authority
In a peer to peer (or P2P) computer network participants are connected with each other, whereby the cumulative bandwidth of network participants is used. P2P networks are typically used for connecting nodes via ad hoc connections. A pure P2P network does not have the notion of clients or servers but only equal peer nodes that simultaneously function as both “clients” and “servers” to the other nodes on the network. Such networks are widely used for sharing content files such as software, audio, video, data or anything in digital format. Real-time data, such as telephony traffic or IPTV, is also passed using P2P technology. The technology itself is legal and applied increasingly in various business models. However, it has also been used for copyright infringements and the dissemination of child sexual abuse images (illegal file sharing).
In parallel computing a is split into smaller programmes to be executed in different processors at the same time. This is way to speed-up the execution of computational tasks and is very useful for complex problems requiring high-intensity processing.
Owns and operates the passive infrastructure
Power line communication carries data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers. A wide range of power line communication technologies are needed for different applications, ranging from home automation to Internet access.
A shared-access technology for FTTH/FTTB
The establishment, operation, control or making available of such a network.
Public Switched Telephone Network
An electronic communications network used wholly or mainly for the provision of publicly available electronic communications services.
A service available to the public for originating and receiving national and international calls and access to emergency services through a number or numbers in a national or international telephone numbering plan, and in addition may, where relevant, include one or more of the following services: the provision of operator assistance, directory enquiry services, directories, provision of public pay phones, provision of service under special terms, provision of special facilities for customers with disabilities or with special social needs and/or the provision of non-geographic services.
The total capital value of the assets used to calculate the costs of the regulated services.
Part of the electromagnetic spectrum corresponding to radio frequencies. For the purpose of the Spectrum Decision, it includes radio waves in frequencies between 9 kHz and 3 000 GHz; radio waves are electromagnetic waves propagated in space without artificial guide.
The envisaged multiannual programme, to be adopted in co-decision, to provide strategic orientations for spectrum policy in the EU.
The facilities associated with the provision of unbundled access to the local loop, notably collocation, cable connections and relevant information technology systems, access to which is necessary for a beneficiary to provide services on a competitive and fair basis.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial number) of an object or person wirelessly, using radio waves. RFID belongs to the broad category of automatic identification technologies. It is in use all around us – for shopping (e.g. tagging of groceries), driving a car (e.g. speeding up transactions on the road), public transport ticketing (e.g. RFID-enabled smart cards in trains and buses, fighting against fraud and/or providing value-added services to travellers), leisure (e.g. secure access and payments in parks, zoos, stadiums, bars/clubs), going to work (e.g. secure access, time registration, evacuation management), crossing borders (e.g. tracking luggage, e-passport), healthcare (e.g. more efficient management, more secure care).
Unlike ubiquitous UPC bar-code technology, RFID technology does not require contact or line of sight for communication.
Rights to install facilities on, over or under public or private property to an undertaking authorised to provide electronic communications networks whether public or not.
In wireless telecommunications, roaming is a general term that refers to the extending of connectivity service in a location that is different from the home location where the service was registered. Regulation on roaming charges in the European Union is a part of policy of the EU promoting competition, safeguarding consumer interests and enhancing digital single market. The current roaming rules aim at increasing competition in the roaming market by structural remedies such as enabling consumers to buy roaming services separately from domestic mobile services and providing in the meantime safeguards to consumers in the form or prices caps within European Union and European Economic Area member states.
Right of Way
Comitology committee established under the 2002 Radio Spectrum Decision for the technical harmonisation of spectrum. The European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) provides technical advice for the work of the committee.
An advisory body composed of High Level officials from the Member States responsible for radio spectrum policy created by the Commission. Advises the Commission (and, following the entry into force of the new regulatory framework, may provide reports and opinions to Parliament and Council) on strategic issues concerning radio spectrum policy.
The concept introduced in the regulatory framework that it is the user of radio spectrum that decides on the electronic communications service that they provide. Exceptions to this have to be justified as necessary for the fulfilment of a general interest objective.
Operators who provide public telecommunications services at large using a third party’s (fixed or wireless) network, excluding fixed voice telephony service providers that do not provide voice telephony within the meaning of Community law, such as simple resellers, calling card service providers and call back operators.
The provision to a beneficiary of access to the local loop or local sub loop of the notified operator, authorising the use of the non-voice band frequency spectrum of the twisted metallic pair; the local loop continues to be used by the notified operator to provide the telephone service to the public.
Significant market power
Sells services (e.g. Internet, TV, telephony, etc.) to the end user
The designation of a given frequency band for use by one or more types of radio communications services, where appropriate, under specific conditions.
The application of State aid rules to public service broadcasting has to take into account a wide number of different elements. The Commission adopted Directive 80/723/EEC of 25 June 1980 on the transparency of financial relations between Member States and public undertakings as well as on financial transparency within certain undertakings. These rules are interpreted by the Court of Justice and the Court of First Instance. The Commission Communication on the application of State aid rules to public service broadcasting sets out the principles to be followed by the Commission in the application of the relevant Articles in the EC Treaty to State funding of public service broadcasting. More information.
Any natural person or legal entity who or which is party to a contract with the provider of publicly available electronic communications services for the supply of such services
Some Member States require film producers receiving State aid to spend a specific proportion of the aid received or of the film budget in the territory of the supporting country. Under the Cinema Communication, the producer must be free to spend at least 20% of the film budget in other Member States without suffering any reduction in the aid provided for under the scheme. In other words, the Commission has until now accepted as an eligibility criteria territorialisation in terms of expenditure of up to 80% of the production budget of an aided film or TV work.
Any data processed for the purpose of the conveyance of a communication on an electronic communications network or for the billing thereof. According to the means of communication used, the data needed to convey the communication will vary, but may typically include contact details, time and location data. Although such traffic data are to be distinguished from content data, both are quite sensitive as they give insight in confidential communications.
Markets identified in accordance with Article 15(4) of the Framework Directive covering the Community or a substantial part thereof located in more than one Member State.
A triple-play network is one in which voice, video and data are all provided in a single access subscription. Quadruple play also contains provision of mobile service.
A Universal Account Number is an 8-digit code, unique to every phone number, that is used to transfer a broadband connection or phone number from one supplier to another.
In order to switch from one ADSL provider to another you will usually need to provide your UAN to your new supplier before they can complete the transfer.
Full unbundled access to the local loop and shared access to the local loop; it does not entail a change in ownership of the local loop.
Market players players; for instance a connection to the public telephone network and access to publicly available telephone services at a fixed location enabling voice and data communications services (including also broadband if so determined at the national level like done so far in FI, MT, ES), comprehensive directory and directory enquiry service, availability of public payphones (operators, providers etc.) as defined under EU law.
The minimum set of services, defined in the Universal Service Directive, of specified quality which is available to all users regardless of their geographical location and, in the light of specific national conditions, at an affordable price.
The provision of a defined minimum set of services to all end-users at an affordable price; for instance a connection to the public telephone network and access to publicly available telephone services at a fixed location enabling voice and data communications services (including also broadband if so determined at the national level like done so far in FI, MT, ES), comprehensive directory and directory enquiry service, availability of public payphones.
Any service which requires the processing of traffic data or location data other than traffic data beyond what is necessary for the transmission of a communication or the billing thereof.
Very-high bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line
A technology used for transmitting standard telephone calls over the Internet using packet-linked routes, from any device, including mobile and fixed line phones.
It is the technique of passing multiple frequencies (wavelength and colours) of light simultaneously across a single fibre, thereby increasing the capacity of installed fibre infrastructure.
Short for wideband CDMA, a high-speed 3G mobile wireless technology with the capacity to offer higher data speeds than CDMA. WCDMA can reach speeds of up to 2 Mbps for voice, video, data and image transmission. WCDMA was adopted as a standard by the ITU under the name “IMT-2000 direct spread.”
Areas where no high capacity broadband infrastructure exists.
International standards for high speed/high bandwidth services over wireless networks, often connecting to the mainstream fixed telecommunications networks.
Wireless local loop: a wireless connection between a telephone exchange and the subscriber’s telephone.
A collective term for all types of digital subscriber lines, including asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL) and high-data-rate digital subscriber line (HDSL).
Wi-Fi is a technology that allows devices like computers, smartphones, wearables, and smart home devices to connect to the internet wirelessly over a local area network (LAN). Using radio waves, typically in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands and 6 GHz bands, WiFi transmits data over short or longer distances, providing internet without using physical cables.
Wi-Fi abilities
Wi-Fi lets you connect multiple devices to the internet without physical cables, offering flexibility in how and where you use your devices around your premises.
Wi-Fi offer speeds that rival traditional Ethernet, supporting streaming, gaming, and large file transfers. Modern WiFi can offer speeds up to 2000Mbps in certain locations
Wi-Fi can offer a very solid range. Depending on the router and environment, WiFi can cover areas ranging from a single room to an entire home.
What can affect Wi-Fi network performance in your home?
To view our full range of Wi-Fi devises visit our shop
How to Get an Accurate Wi-Fi Speed
We recommend you plug your devices directly into an Ethernet port Lan or Wan on Digiweb’s modem when running an internet speed test. It’s important to test your internet speed where you typically use your computer or a laptop. If you plug your device directly into Digiweb’s router and use your browser to visit sites like Speedtest.net, Fast.com, you will be able to see your most accurate download speeds.
Please note that you can also run Wi-Fi internet speeds by connecting your smart device to Digiweb’s modem. The result of such speed test will also depend on your own device and if the device is compatible with Wi-Fi6 or Wi-Fi7.
Wi-Fi Bands
These are the different Band’s (radio frequency) that broadcast from the modem
2.4GHz
5GHz
6GHz
Not all devices can connect to all the Wi-Fi bands. Older devices may not be able to connect to 6GHz
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest generation of WiFi technology, designed to improve speed, efficiency, and capacity compared to previous standards (like WiFi 5, or 802.11ac). It’s particularly beneficial in environments with many connected devices, like homes, offices, and public spaces, where network congestion can slow down connectivity.
To view our full range of Wi-Fi devices visit our shop
Practical FRITZ!Apps add new functions to your FRITZ!Box, smartphones and tablets.
With FRITZ!Apps you can carry your home network along in your pocket. Access your FRITZ!Box from anywhere via Smartphone or tablet or make calls with your mobile over the landline rate when you’re in your WiFi reception area – all this and more is possible with FRITZ!Apps. Available as a free download for Android and iOS. Fritz!Apps include: Fritz!Apps, Fritz!Box, Fritz, MyFRITZ!App, FRITZ!App Fon, FRITZ!App Media, FRITZ!App Cam, FRITZ!App TV, FRITZ!App WLAN and FRITZ!App Ticker
With the FRITZ!Box you can also send and receive faxes without an external fax machine. The FRITZ!Box receives the faxes and forwards them as PDF files named after the reception date and time via email and/or saves them on a USB storage device in the folder “FRITZ\faxbox”. When sending faxes, you enter the text in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest Fritz!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
If you want to use an internet telephone number for faxing, then you must enable T.38 (fax over IP) for fax transmission in the FRITZ!Box. With T.38, a special network protocol is used for fax transmission instead of fax tones. As a result, transmission is significantly less susceptible to interference:
In the next step, you may be asked to enter various email account information. This information is required if you want the FRITZ!Box to forward new faxes via email and the push service has not been configured yet. Enter the email account information as follows:
Note:The email account information can be edited any time under “System > Push-Service > Sender” in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
If you selected several telephone numbers for receiving faxes, then you can assign each of these telephone numbers a different email address to which faxes are then forwarded:
Note:Faxes that are forwarded from a telephone connected to the FRITZ!Box to an answering machine are forwarded to the email address(es) assigned to the first fax number.
Configuring a USB storage device connected to FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box allows you to use USB storage devices connected to it as a central storage location in the home network (“Storage (NAS)”). Then all of the computers, smartphones, and other devices connected to the FRITZ!Box can easily access your files with a web browser or using the Server Message Block protocol (SMB), for example with the Windows Explorer on Windows computers.
In addition, you can set up a secure internet sharing for the USB storage devices. This allows you to access your files from the internet at any time.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
You can only access a USB storage device connected to the FRITZ!Box with more than one device at the same time if the device is not configured for use with the USB remote connection software:
To access storage (NAS) contents, you need a user account with a user name and password. Set up a FRITZ!Box user in the FRITZ!Box for this purpose:
The FRITZ!Box is already password protected in the factory settings. If you disabled the FRITZ!Box’s password protection, reenable it:
There are several ways to access USB storage devices connected to the FRITZ!Box. Which method makes most sense depends on whether you are in your home network or want to access the storage device when you are away from home, and whether you are using a computer, or a smartphone or tablet:
Accessing storage (NAS) in the home network
In the home network, you can use a web browser to easily access USB storage devices connected to the FRITZ!Box via http://fritz.nas.
If you would to prefer to use the Windows Explorer, macOS Finder, or another application that uses the Server Message Block protocol (SMB), you can also configure the USB storage device connected to the computer as a network drive.
If you are using a smartphone or tablet with Android or iOS, MyFRITZ!App not only allows you access USB storage devices, you can also use it to check calls, voice messages, and other events, control your smart home devices, and check the power consumption of the connected devices at any time.
Accessing storage (NAS) over the internet
When you are away from home, you can also access USB storage devices connected to the FRITZ!Box over the internet at any time by means of a secure internet sharing. However, we recommend using MyFRITZ!App with a smartphone or tablet.
If you only want to allow other users to access certain files or folders, you can simply share them by means of an access link. This way you can allow friends and relatives to access your pictures and videos from your last vacation without allowing them to change or delete files from the USB storage device, for example.
If you prefer to use an FTP client such as Cyberduck, FileZilla, or WinSCP instead of a web browser, you can also access USB storage devices connected to the FRITZ!Box via FTP/FTPS when you are away from home.
In the home network you can either use a USB printer connected to the FRITZ!Box as a network printer, or use it with the USB remote connection software. Which operating mode is preferable depends on your requirements and the USB printer you are using.
The FRITZ!Box Media Server (UPnP AV server) provides all of its functions in accordance with the DLNA guidelines. However, it is not officially DLNA certified. Whether AVM shall seek DLNA certification for the FRITZ!Box, and, if so, when, has not yet been decided.
Note:The Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) is an association of computer, smartphone, and consumer electronics manufacturers. Their goal is to guarantee compatibility between different devices and applications for digital entertainment. To achieve this, the DLNA issues technical guidelines and certifies devices and applications that comply with these guidelines.
In the FRITZ!Box you can define which network devices and applications are to be treated with high priority or low priority when they access the internet. This way you can ensure optimal reaction times for online games even if peer-to-peer services are using the internet connection at the same time. This type of prioritization of applications is also called Quality of service (QoS).
Note the following information on the FRITZ!Box’s various prioritization categories and proceed as described in the subsequent measures.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
There are various ways to prioritize different network devices and applications in the FRITZ!Box. Three categories are available:
Real-time applications
Network devices and applications prioritized in the category “Real-time Applications” are always allocated as much internet connection throughput as needed. If other applications are using the internet connection at the same time, data sent by real-time applications is always sent first.
If several real-time applications are using the internet connection at the same time, then the throughput is divided between them equally. The application “Internet telephony” (VoIP) is an exception; this real-time application always has the highest priority, even over other real-time applications.
Note:If a real-time application requires the entire throughput, then other applications cannot transmit data at the same time.
The category “Real-time Applications” is especially suitable for applications with very high demands on throughput and reaction times such as internet telephony, IPTV, or video on demand.
Prioritized applications
As long as the internet connection is not overloaded by real-time applications, network devices and applications in the “Prioritized Applications” category can use up to 90% of the upload throughput. Devices and applications that are not prioritized are then allocated 10% of the upload throughput when prioritized applications are transmitting data at full capacity.
If several prioritized applications are using the internet connection, then the throughput is divided equally. The category “Prioritized Applications” is suitable for applications that require fast reaction times, such as VPN and terminal applications, or online games.
Background applications
Network devices and applications assigned to the category “Background Applications” are always treated with the lowest priority when the internet connection is working at full capacity. If another application requires the entire internet connection throughput, all background applications must wait until capacity becomes available again.
If the internet connection is not being used by any other application, then the background applications can use the entire throughput.
The category “Background Applications” is suitable for automatic updates and peer-to-peer services, for example BitTorrent.
If you configure a prioritization rule for a network device, then it applies to all applications executed on this device:
When you configure a prioritization rule for a specific network application, you can decide whether the rule should apply to all or only specific network devices on which the respective application is running:
The FRITZ!Box’s wireless guest access offers your guests separate internet access. Devices in the guest network are denied access to devices in the home network. For this purpose, the FRITZ!Box provides an additional wireless network (WiFi) with its own security settings and a captive portal, if needed.
You can either offer encrypted or unencrypted guest access:
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
All devices in the guest network are assigned the “Guest” access profile in the FRITZ!Box parental controls. You can adjust the “Guest” access profile, for example if you want to limit internet use in the guest network to certain times or block access to certain websites:
If your debit card reader has a network port or is equipped with wireless LAN (WiFi), you can simply connect it to a LAN port or the wireless network of your FRITZ!Box and use it to read debit cards.
Note:If your debit card reader only has an analog port, you can configure the debit card reader as a telephony device in the FRITZ!Box.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
In the factory settings, the FRITZ!Box automatically assigns the correct IP settings to all devices via DHCP. If you disabled the FRITZ!Box’s DHCP server, reenable it:
Make sure that the debit card reader automatically obtains its IP settings from the FRITZ!Box (this is the standard setting for most debit card readers):
The debit card reader is now connected to the FRITZ!Box and can be used to read debit cards.
You can simply use a network cable or wireless LAN (WiFi) to connect an IP camera (network camera) to your FRITZ!Box. Then you can easily follow what is happening in front of the camera with a web browser or an app, either in the home network or via the internet when you are away from home.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
In the factory settings, the FRITZ!Box automatically assigns the correct IP settings to all devices via DHCP. If you disabled the FRITZ!Box’s DHCP server, reenable it:
Make sure that the IP camera obtains its IP settings from the FRITZ!Box:
The IP camera is now connected to the FRITZ!Box and is available to the entire home network.
Note:Refer to the manufacturer for further information on how to set up the IP camera and access it.
The following steps are only necessary if you want to access the IP camera over the internet when you are away from home or grant friends internet access to the IP camera:
Some IP cameras can not only automatically save images on the SD card in the camera, they can also transmit images to an FTP server or use the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol to save them to storage in the home network.
Only perform the following steps if your IP camera can save images to an FTP server or network shares and you want to save the images to a USB storage device connected to the FRITZ!Box:
How do I block numbers from being called?
To block numbers you will have to call our customer care team to add call bar on the line.
Call 1902
You can also contact us on support@digiweb.ie customercare@digiweb.ie
For WLR information including how to check Landline number, Check Provider, Call Forwarding and Voicemail please refer to the following reference
To check your landline number, dial 199000 and an automated voice will call your telephone number back to you.
To check who your provider is, dial 19800 for Local call provider, 19801 for National Call provider and 19822 for International call provider. For Smart Telecom Customers you will get a message staring with SMART TELECOM, followed by 2-4 digits
To access your voicemail, dial 171 from your landline and enter your password. Your voicemail password by default is 1234.
To change passwords:
At the main menu press 4
Press 2 for Administrative Options
Press 1 to change the password
Enter the password and press # to confirm.
Greetings – Personal, Standard and Extended Absence Greeting
To change the greeting: At the main menu press 4 for Personal Options Press 3 for Greetings:
Press 1 to change the Personal Greeting
To check your voicemail when you are not at home, call your landline number and when you start to hear the message for voicemail press the # button on your phone and wait to hear the recorded messages.
Greetings – Personal, Standard and Extended Absence Greeting
To change the greeting: At the main menu press 4 for Personal Options Press 3 for Greetings:
Press 1 to change the Personal Greeting
• Press 1 for standard or 2 for personal greeting, or Press 2 for extended absence Greeting
• record your greeting and then press #, or Press 3 for Name
• Record your name and then press
You can simply use a network cable to connect a NAS (Network Attached Storage) system to your FRITZ!Box, making it available to the entire home network as well as other users in the internet. Since the NAS system itself makes data stored on it available, you do not have to configure any specific settings for it in the FRITZ!Box.
Note:All instructions on configuration and settings given in this guide refer to the latest FRITZ!OS for the FRITZ!Box.
In the factory settings, the FRITZ!Box automatically assigns the correct IP settings to all devices via DHCP. If you disabled the FRITZ!Box’s DHCP server, reenable it:
Make sure that the NAS system obtains its IP settings from the FRITZ!Box:
The NAS system is now connected to the FRITZ!Box and is available to the entire home network or users in the internet.
Note:Refer to the manufacturer for further information on how to set up the NAS system and access it.
The following steps are only necessary if you want to access the NAS system over the internet when you are away from home or grant friends internet access to the NAS system:
Digiweb guarantee 100% broadband coverage nationwide for your home or business.
Don’t worry if your home is not yet Fibre enabled. Order any Digiweb Broadband Plan and you’ll receive our Fibre Guarantee. We’ll check your telephone line at least once every 3 months and we’ll get in touch with you once your premises are fibre enabled.
We have your interest at heart and work passionately to provide you with the best possible service wherever you live in Ireland. One less thing to worry about
How it works: When your friend connects to Digiweb Broadband and has paid their first 2 invoices in full, we will credit both of your accounts with €30. Referring customer (you) must not have any invoices outstanding. There’s no limit to how much you can earn, so refer as many friends and/or family members as you like to earn even more. This excludes relocation of same account. Further terms and conditions may apply.
Terms & Conditions: To receive the “Refer a Friend” credit you must be a Digiweb customer who’s account is not in arrears. At the time of referral, your friend must not have been recommended by another Digiweb customer or who’s availed of another special offer when joining Digiweb. Credits are applied to your account and theirs once your friend has paid their first month subscription fee to Digiweb.
VOIP is an acronym for Voice over Internet Protocol, a method of making calls via Internet Protocol (IP) networks. VoIP is also known as Internet telephony, IP telephony, or broadband telephony. Depending on the type of VOIP service you have, you can make a VOIP call from a computer or other internet enabled devices.
Yes, this feature is known as Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR). You can request for this ancillary service to be activated via the Customer Care or Technical Support Departments. Please Freephone 1902.
Yes. Please remember that your VoIP services requires electricity to work. If there is a total power cut/failure in your home or business then the phone service would also stop working.
Yes – existing phone numbers can be ported and there is no charge for this service.
Click here to download the form to move your phone number to Digiweb VoIP
No, unfortunately Digiweb cannot guarantee the successful operation of Fax over the Digiweb Broadband Talk (VoIP) service. However, general one page Faxes should be fine. Please note for UK DECT phones/fax machines, you need the UK cable and a proper UK/Irish adaptor with ringing capacitor built in.
No. We do not offer a backup power facility but our Technical Support team can request a call divert to a local, national or Irish mobile number of your choosing where you experience a power cut. Please note that these calls may be charged where outside of any call bundle minutes you have with Digiweb.
To avoid loss of service due to a loss of electricity or power cut, you can purchase an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) online or from your local electrical / PC store. A UPS connected to your Digiweb Broadband equipment will provide the necessary power in the event of a loss of electricity or power cut.
No. Digiweb can provide you with a new geographical number such as 01 or 021 for example. There is no charge for this
Yes. The provided Digiweb modem must be powered on and connected to the Internet at all times for your VoIP service to work. In the event of a loss of electricity / power cut / Broadband supply problem, your Digiweb VoIP phone service will not work. You will not be able to make emergency phone calls.
To avoid loss of service due to a loss of electricity or power cut, you can purchase an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) online or from your local electrical / PC store. A UPS connected to your Digiweb B
FTTH Installation process
When you order a new FTTH connection from Digiweb, an engineer working for KN Group will visit your home at a time agreed by you to complete the fibre first installation. FTTH will be brought into your home either overhead or underground and into the telephone socket. Some slight drilling is involved on the day.
For more see the video below:
SIRO Installation process
When you order a new SIRO connection from Digiweb, an engineer working for Actavo or TLI will visit your home at a time agreed by you to complete the fibre first installation. SIRO will be brought into your home either overhead or underground and into the ESB meter box. Some slight drilling is involved on the day.
Please see this video for a full SIRO installation process:
NBI FTTH Installation process
When you order a new connection NBI from Digiweb, an engineer working for KN Circet will visit your home at a time agreed by you to complete the fibre first installation. NBI FTTH will be brought into your home either overhead or underground. Once this is agreed, the engineer will discuss with you where you would like the cable to enter your premises. We will place a small NBI™ network unit on the wall inside your premises that will connect to Digiweb’s modem.
Some slight drilling is involved on the day.
For more see the video below:


